 The
Halo Plug is Unique
The
Halo Plug is Unique The
Halo Plug is Unique
The
Halo Plug is Unique
The
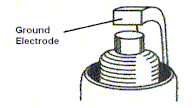
spark plug is virtually unchanged in design since its development in the early
part of this century. The standard plug is an imprecise instrument that is a
necessary part of the combustion process. It consists generally, of a center
firing electrode inserted into an alumina ceramic insulator, both of which are
inserted and sealed in a threaded metal shell. The ground electrode consists of
a piece of rectangular wire welded to the edge of this metal shell, and formed
over to cover the top of the firing electrode with a specified gap.
Improvements to the design to date have consisted of larger gaps, longer reach center electrodes, multiple electrodes, and precious metal electrodes, all geared to improve the life of the plug, and increase the fuel burning efficiency. However, these items basically all treated the symptom, versus correcting the reasons for these deficiencies.
What is different about Halo Plug?
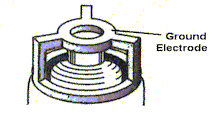
The patented Halo design however, is a completely new technology that actually makes the spark plug an integral precise part of the combustion system.
The Halo
The Halo Plug consists of a circular ring attached to posts above a lower ring that is mounted to the metal shell of the spark plug (less the standard side-wire electrode). The entire structure is molded into one piece. This design possesses numerous advantages over standard and premium spark plugs.
Less plug fouling and erosion
The nature of the location of the upper ring with respect to the center electrode allows multiple firing paths. This eliminates the point erosion (and consequent degradation in performance - usually beginning at about 2,000 miles) evident on standard spark plugs. This erosion has typically been addressed by providing firing surfaces with metals that exhibit improved wear characteristics. With the Halo design, plug life is extended by virtue of the performance of the plug, and adding these better wearing metals will only enhance an already vastly improved plug life.
Multiple firing pathsThe multiple firing path performance characteristic of the HaloTM design resists plug fouling, since alternate paths can be found in the event deposits begin to form on the center electrode. If these deposits occur on a standard plug, it often inhibits or prevents firing, since another path is less likely to be found. The open configuration also aids in cleaning of the center electrode, further reducing the possibility of deposits.
Fuel has a direct path to the spark
The open ring provides a direct path to the spark for the air/fuel mixture being pushed up toward the plug from the piston. This direct exposure eliminates the "quenching effect" The quenching effect is a characteristic of standard plugs, where the mixture is shielded from the spark by the conventional side-wire electrode.
Improved gas mileage
The more efficient burning of the mixture also reduces the amount of fuel required, thus improving fuel economy in many vehicles.
The gap
Halo plugs are the only true factory preset gap plugs that cannot be changed inadvertently (within reason). The three legs supporting the upper ring form a tripod that is superior structurally to any other design. The gap cannot be changed by a bump from handling during shipment, bumping during installation, or even a minor drop. The nature of the tip fabricating process also eliminates any internal stresses that would tend to relieve and move as the metal is heated thereby assuring the optimum gap is maintained during all conditions.
It is
new
The
Halo Plug is not yet available in stores. As of July 2000 about
80% of car, truck and
van motors plugs are available. Small
engine plugs are just now available.
Motorcycle, marine and other applications are to follow.
The
Halo Plug has been recognized by the United States Patent Office
as unique allowing several patents and claims. There are also multiple
international patents.
The
Halo ground electrode design is covered by one or more of the following U.S. and
international patents:
|
United
States |
5,280,214 |
|
United
States |
5,430,346 |
|
Australia |
AU-B-75309/91 |
|
Mexico |
182430 |
|
European
Patent Specification |
PCT/EP90/01738 |
|
Germany |
DE
690 24 480 T 2 |
|
France |
UPI-FRE-1/us |
|
United
Kingdom (Great Britain) |
EP
0451264 |
|
Canada
(patent pending) |
BP
# 6220-009 |
|
Several
others are pending. |
|